Network Acceleration Service
1. Introduction to Network Acceleration
The Network Acceleration feature is used to accelerate access to specified foreign academic websites [limited to instances created on the GpuGeek platform]. Compared to Academic Resource Acceleration, it provides a more stable service.
The currently available accelerated addresses are listed below. If the address you require is not included, you can go to the GpuGeek console Submit a Ticket and fill in the domain or address you wish to add. After the platform evaluates the compliance of the domain or address, it will be added for acceleration.
google.com
google-analytics.com
github.com
githubusercontent.com
huggingface.co
hf.co
nvidia.com
r8.im
replicate.com
python.org
pypi.org
pythonhosted.org
pytorch.org
docker.com
docker.io
nvcr.io
gcr.io
quay.io
k8s.io
ghcr.io
2. Purchase Traffic Package
-
Go to the Network Acceleration console.
-
Click to purchase a traffic package.
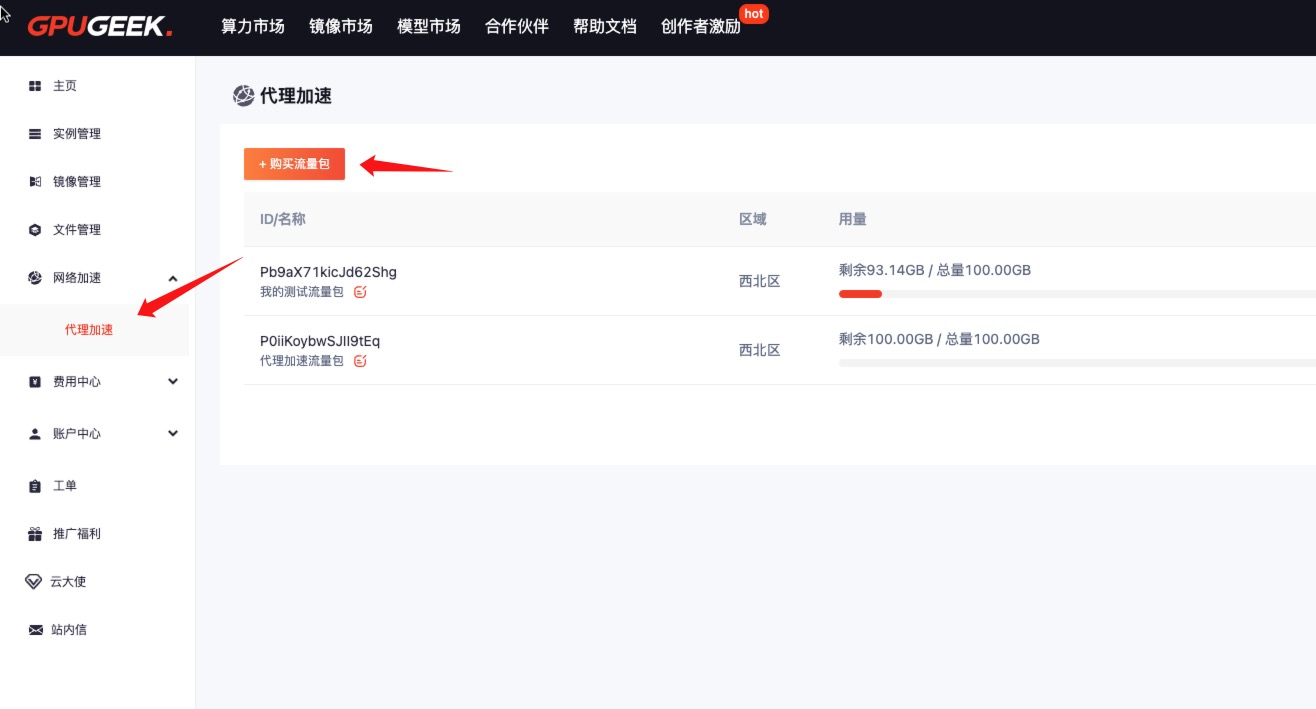
-
Click Add Traffic Package.
- Applicable Region: Currently available in Northwest Region, and can be used by all instances created in Northwest Zone 1 and Zone 2. New applicable regions will be launched gradually.
- Validity: The validity period starts from the purchase date.
- Choose Traffic Package: Select the total size of the traffic package. Prices vary and can be chosen as needed.
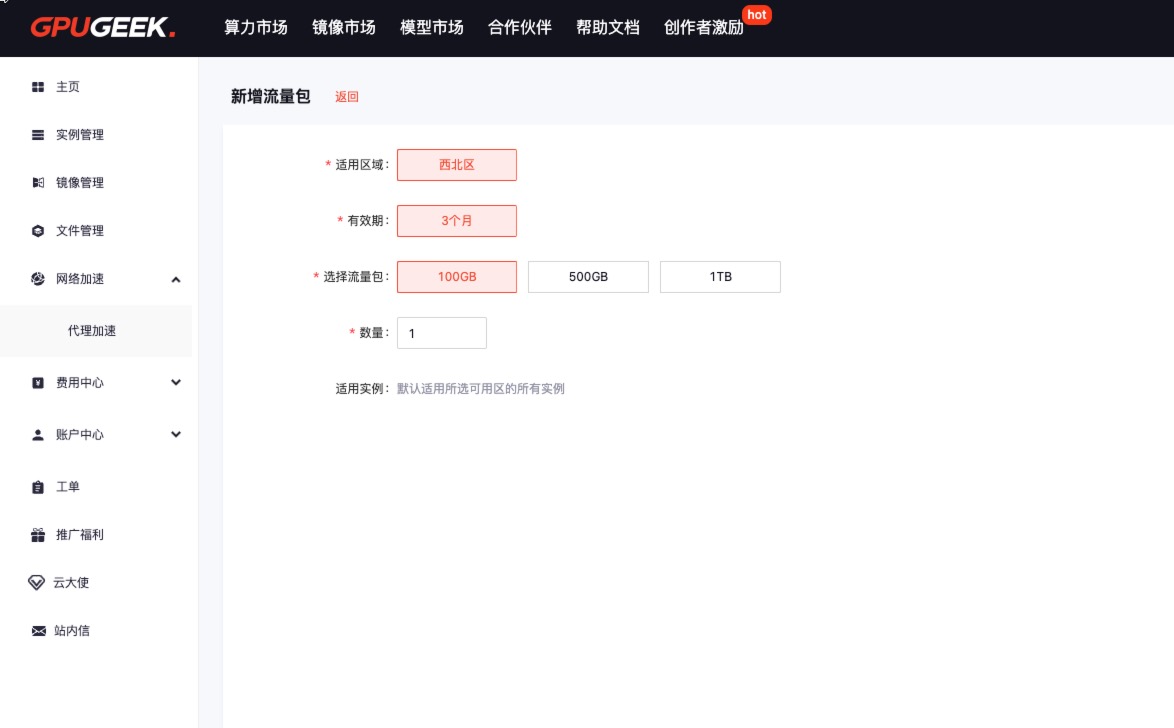
-
Click Purchase Now in the bottom right corner. After purchase, it will appear as shown below:
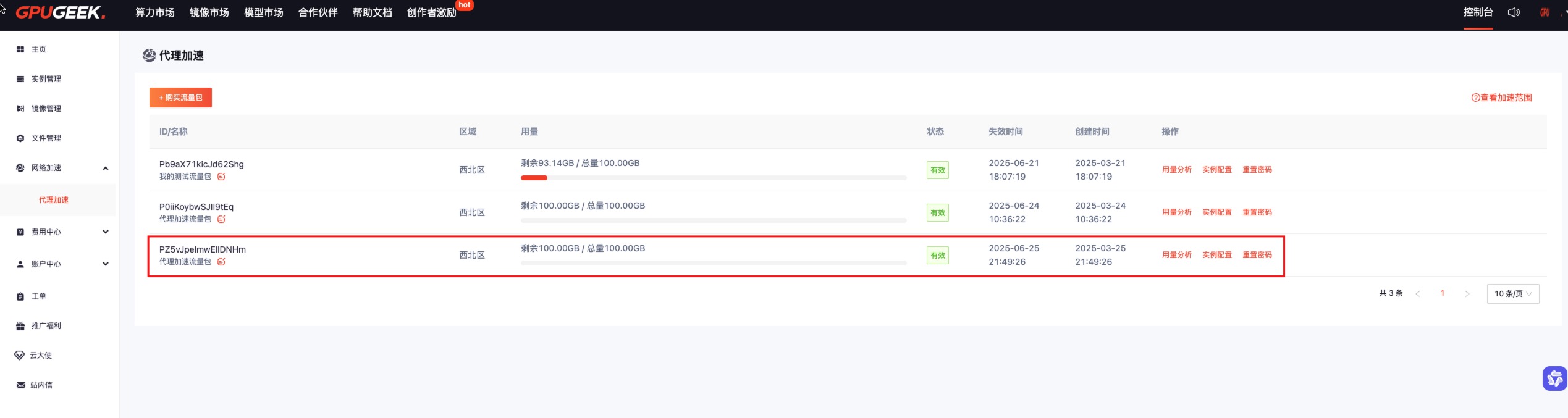
3. Use Traffic Package in Instances
- Click Instance Configuration.
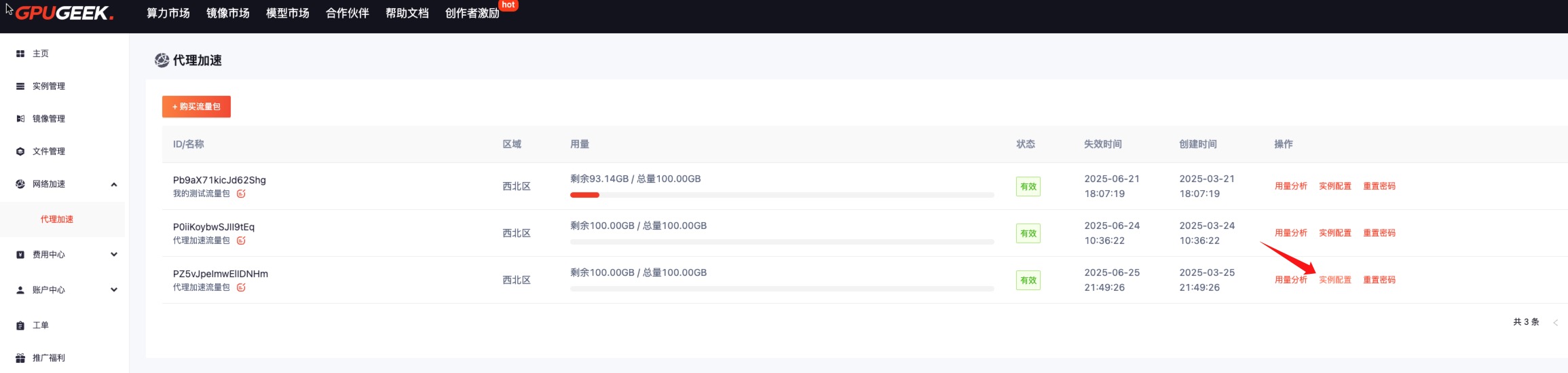
Two configuration methods are available: Temporary Configuration and Permanent Configuration.
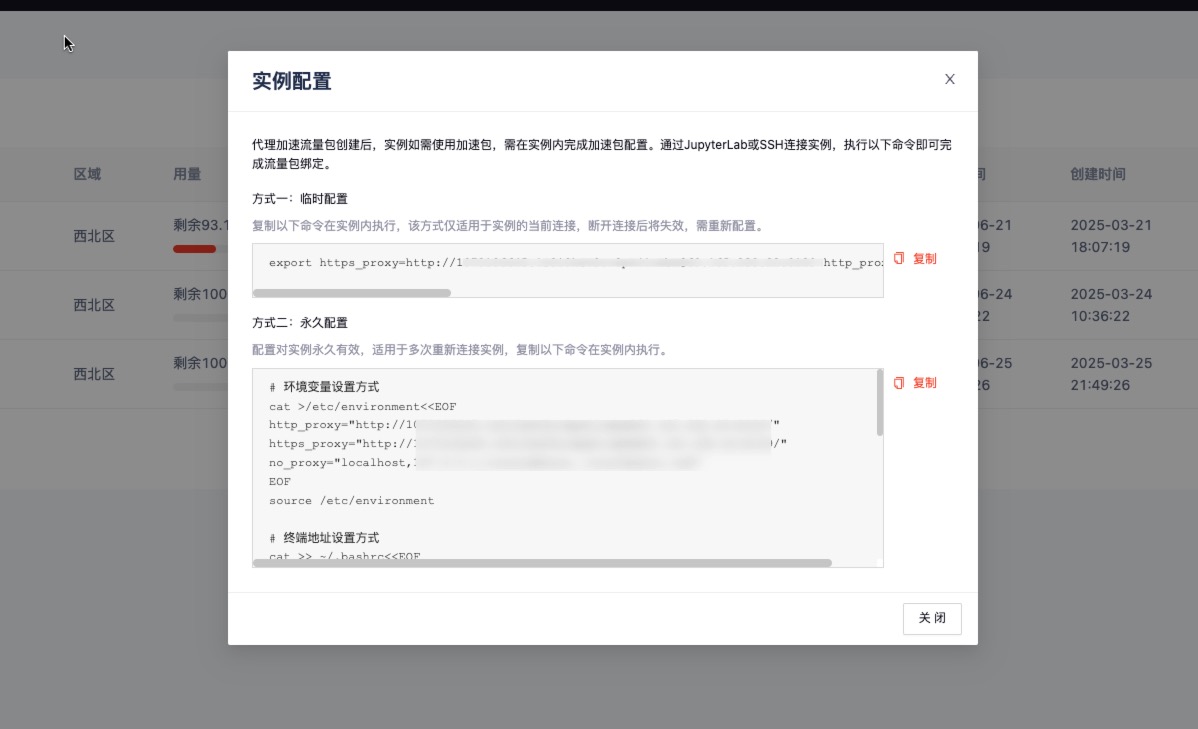
3.1 Temporary Use in Instance
This method only applies to the current connection of the instance. Once disconnected, it becomes invalid and must be reconfigured.
After logging into the instance terminal via SSH, go to Network Acceleration and copy the Temporary Configuration.
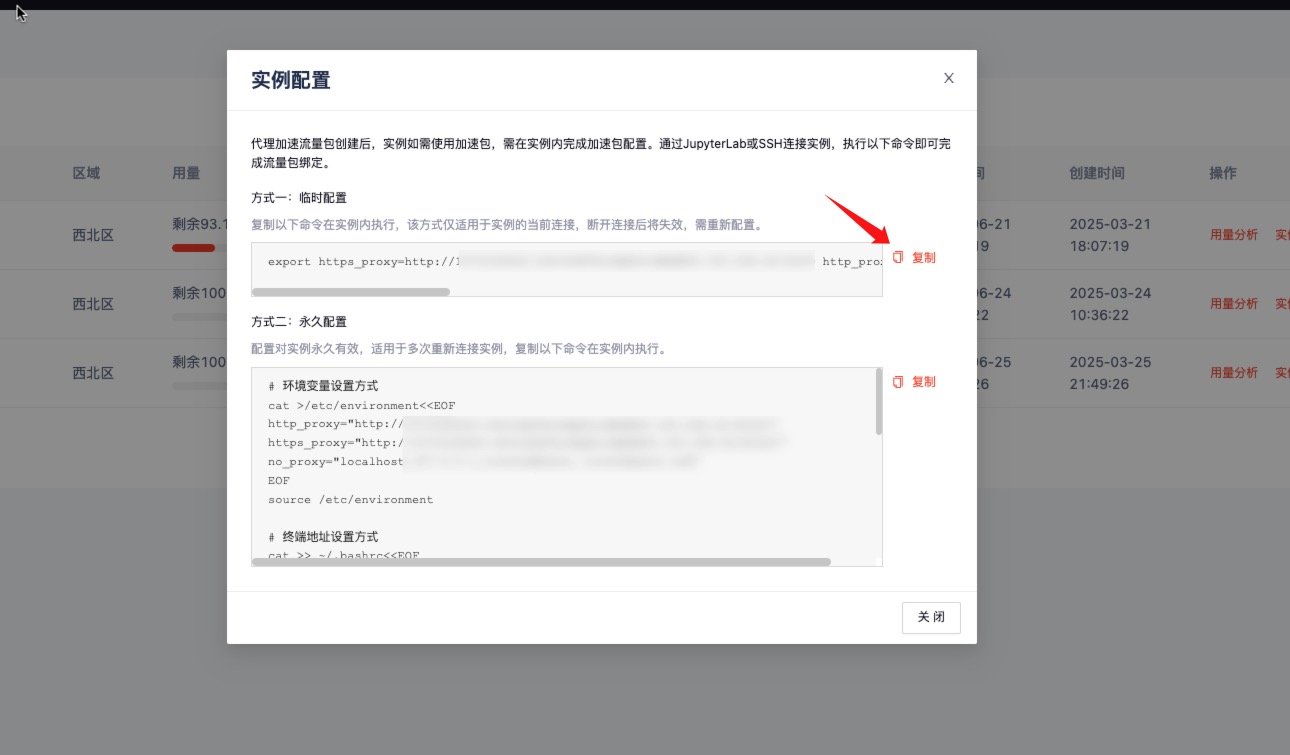
Paste the copied temporary command into the terminal and press Enter.
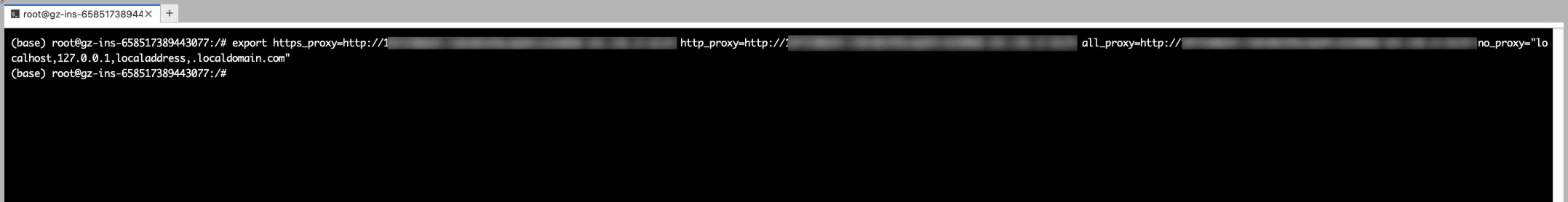
Verify Network Acceleration
(base) root@gz-ins-658517389443077:/# git lfs install
Git LFS initialized.
(base) root@gz-ins-658517389443077:/# git clone https://huggingface.co/Qwen/Qwen2.5-1.5B-Instruct
Cloning into 'Qwen2.5-1.5B-Instruct'...
remote: Enumerating objects: 31, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (28/28), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (28/28), done.
remote: Total 31 (delta 11), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 3 (from 1)
Unpacking objects: 100% (31/31), 3.60 MiB | 2.23 MiB/s, done.
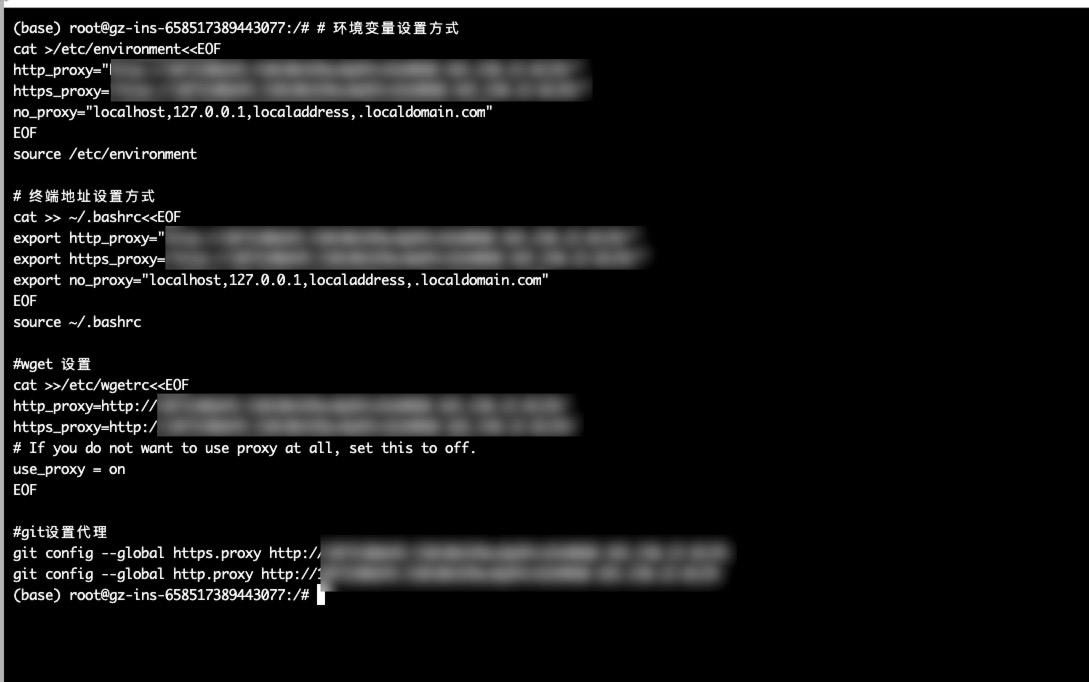
3.2 Permanent Use in Instance
This method is permanently valid for the instance and applies across multiple reconnections. Copy and execute the following commands in the instance.
After logging into the instance terminal via SSH, go to Network Acceleration and copy the Permanent Configuration.
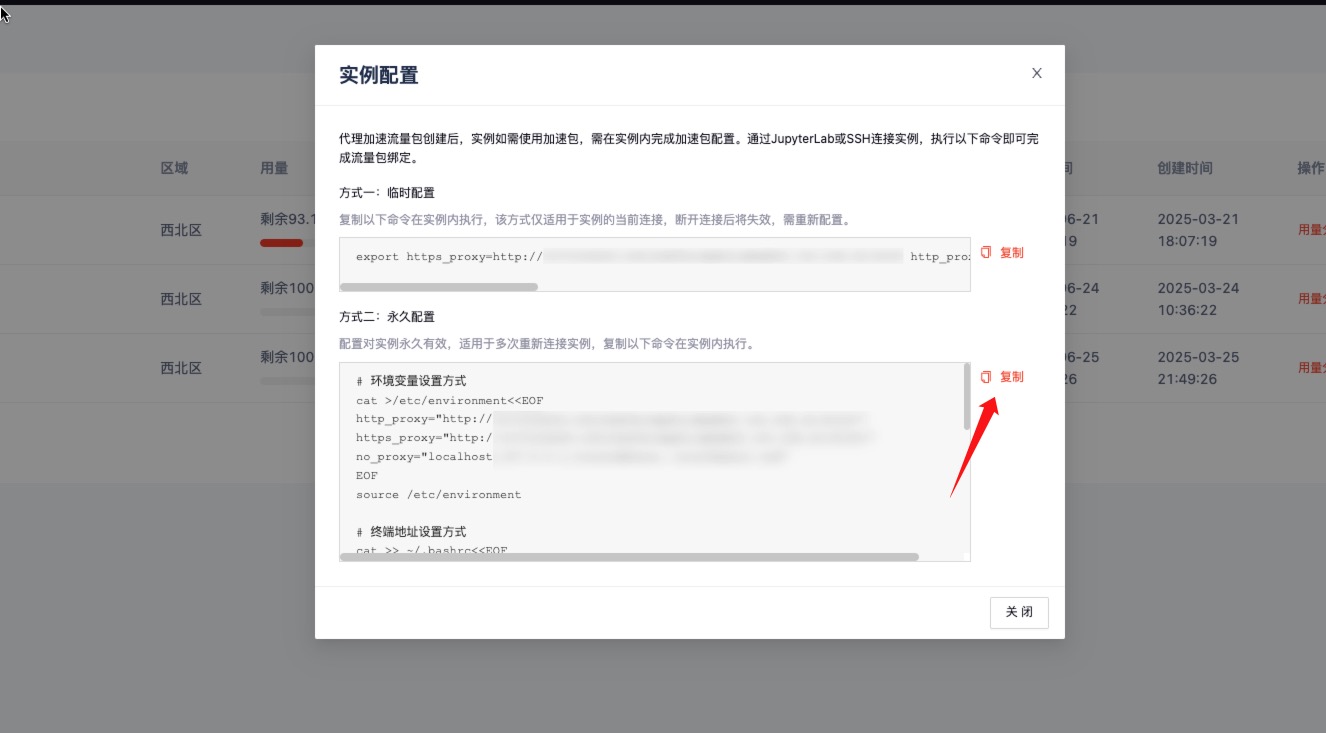
Paste the copied permanent command into the terminal and press Enter.
Verify Network Acceleration
(base) root@gz-ins-658517389443077:/# git clone https://huggingface.co/Qwen/Qwen2.5-1.5B-Instruct
Cloning into 'Qwen2.5-1.5B-Instruct'...
remote: Enumerating objects: 31, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (28/28), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (28/28), done.
remote: Total 31 (delta 11), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 3 (from 1)
Unpacking objects: 100% (31/31), 3.60 MiB | 2.15 MiB/s, done.
After reopening an SSH window or restarting the instance, use the proxy again to verify permanent effect.
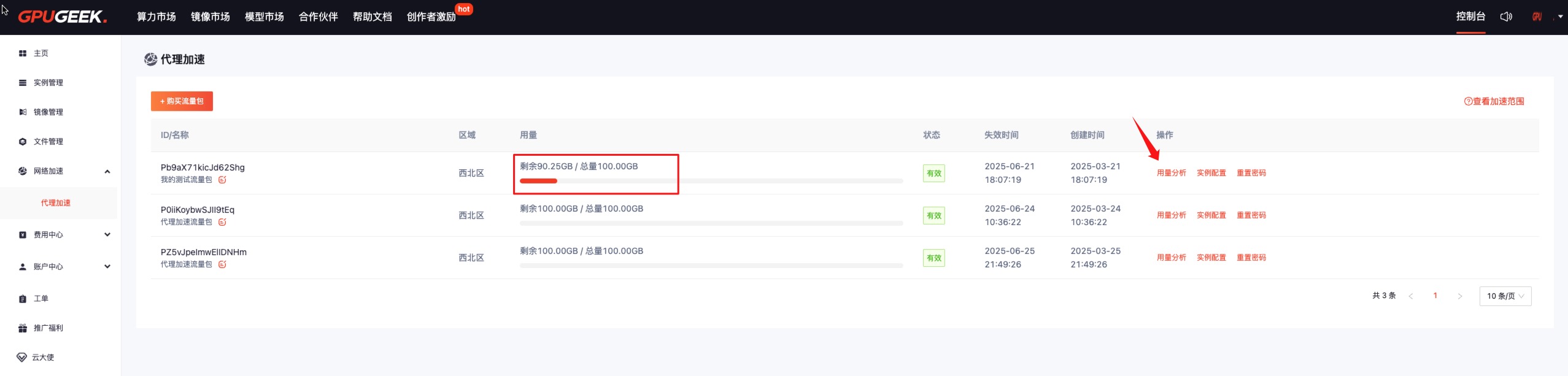
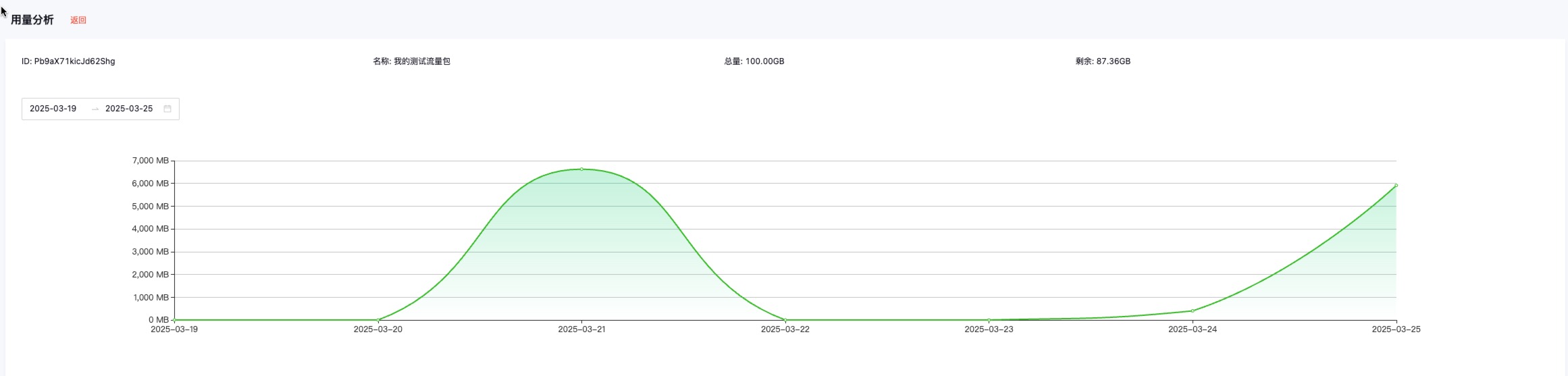
4. Usage Analysis
In the Network Acceleration interface, you can view usage information visually, or click Usage Analysis to check detailed usage.
5. Remove Proxy Traffic
If you no longer need to use the proxy traffic package, you can remove it with the following commands. After removal, traffic package data will no longer be consumed.
Remove Temporary Proxy
unset https_proxy && unset http_proxy && unset all_proxy && unset no_proxy
Remove Permanent Proxy
unset https_proxy && unset http_proxy && unset all_proxy && unset no_proxy
sed -i 's/http_proxy/#http_proxy/g' /etc/environment
sed -i 's/https_proxy/#https_proxy/g' /etc/environment
sed -i 's/no_proxy/#no_proxy/g' /etc/environment
sed -i 's/http_proxy/#http_proxy/g' ~/.bashrc
sed -i 's/https_proxy/#https_proxy/g' ~/.bashrc
sed -i 's/no_proxy/#no_proxy/g' ~/.bashrc
sed -i 's/http_proxy/#http_proxy/g' /etc/wgetrc
sed -i 's/https_proxy/#https_proxy/g' /etc/wgetrc
sed -i 's/use_proxy/#use_proxy/g' /etc/wgetrc
git config --global --unset http.proxy
git config --global --unset https.proxy